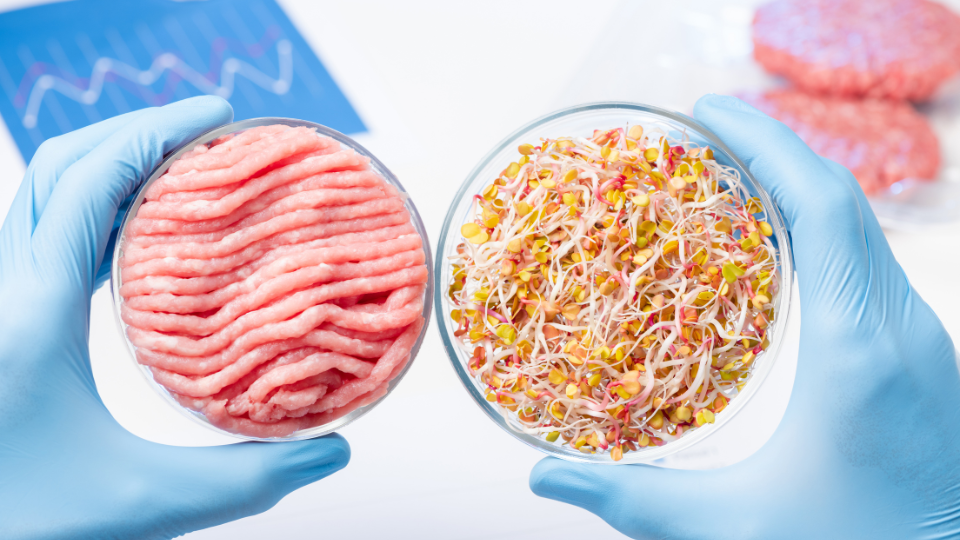
Are you tired of hopping from one diet trend to another, searching for the magic solution to improve your health and manage your weight? Well, look no further because a recent study conducted by the esteemed National Institutes of Health (NIH) has compared two contrasting diets that might just hold the key.
Picture this: You're standing at a fork in the road, with one path leading you toward a low-fat, plant-based diet and the other guiding you toward a low-carb, animal-based diet. Which one should you choose?
Let's dive into the findings of this groundbreaking study and discover which path has more beneficial effects, and is more likely to lead you toward optimal health.
The NIH study aimed to tackle an important question - how do these two diets impact our ad libitum energy intake? In simpler terms, which diet allows us to eat without restriction while still achieving our desired results?
By comparing individuals following a low-fat, plant-based diet with those on a low-carb, animal-based diet, researchers were able to shed light on which approach may be more effective for improving overall health and managing weight.
So if you've ever found yourself wondering what kind of food choices will best nourish your body while keeping those extra pounds at bay, this study is here to provide some valuable insights that could transform your relationship with food forever.
Comparison of Diets
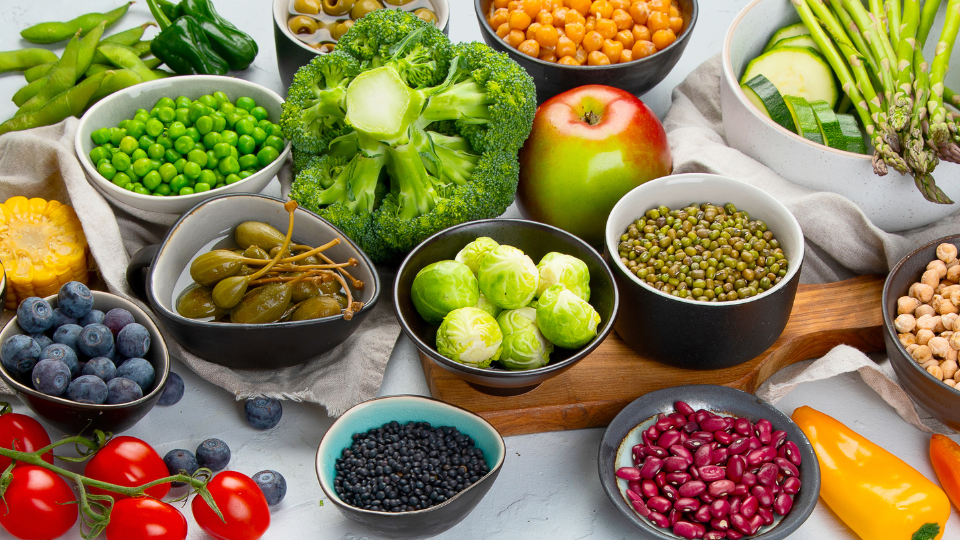
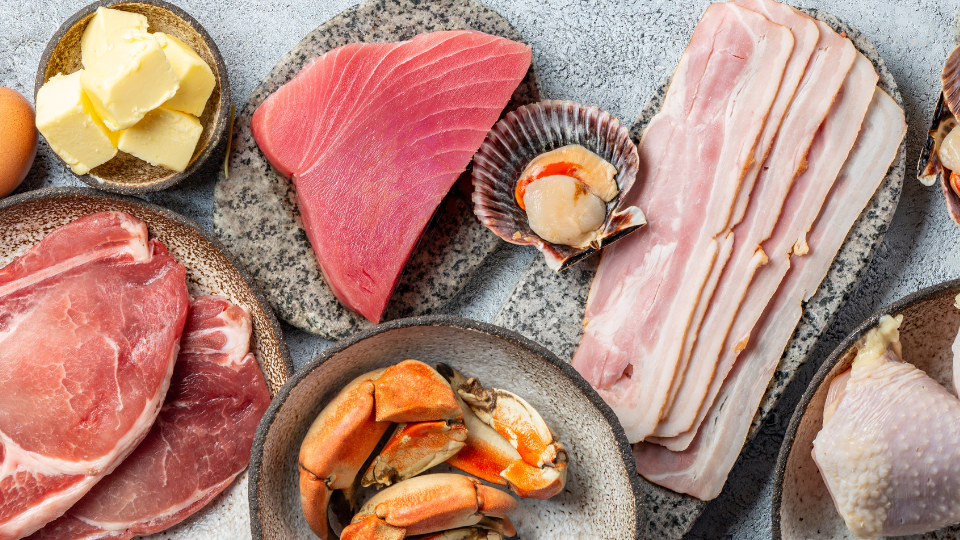
Numerous studies have been conducted to evaluate the benefits of different diets on our body weight and overall health. In this particular study, researchers compared the effects of a low-fat, plant-based diet to a low-carb, animal-based diet.
The results of this study showed that individuals following a low-fat, plant-based diet experienced significant improvements in their body weight and overall health. They were able to lose more weight compared to those on a low-carb, animal-based diet.
Not only did they shed pounds more effectively, but they also experienced additional health benefits such as improved insulin sensitivity, optimized blood sugar levels, improved metabolic effects, and reduced risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes.
On the other hand, individuals following a low-carb, animal-based diet did not experience as much success in terms of weight loss or overall health improvement.
Although they may have initially lost some weight due to restricted carbohydrate intake, it was found that this type of diet can lead to an increased risk of certain health problems, such as high cholesterol levels and cardiovascular diseases.
When it comes to choosing between a low-fat, plant-based diet or a low-carb, animal-based diet for optimal health and well-being, the evidence strongly suggests that the former is superior.
Not only does it promote effective weight loss, but it also provides numerous additional health benefits, such as improved insulin sensitivity and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Energy Intake Comparison
When comparing the effects of a low-fat, plant-based diet to a low-carb, animal-based diet on energy intake, there are some notable differences. Research has shown that individuals following a low-fat, plant-based diet tend to consume fewer calories per day compared to those following a low-carb, animal-based diet.
In one study comparing these two dietary approaches, participants on the low-fat, plant-based diet consumed an average of 500 fewer calories per day than those on the low-carb, animal-based diet. This reduction in calorie intake can be attributed to several factors.
Firstly, plant-based diets tend to be higher in fiber and water content due to their emphasis on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds. These foods have lower calorie densities and provide greater satiety for longer periods of time.
Additionally, the lower fat content in a plant-based diet may also contribute to reduced calorie intake. Fat is more calorie-dense compared to carbohydrates and protein.
By reducing fat consumption and focusing on nutrient-rich foods instead, individuals may naturally consume fewer calories without feeling deprived or hungry.
This difference in calorie intake between the two diets can have significant implications for weight loss efforts. A reduction in daily calorie consumption by 500 calories can lead to about one pound of weight loss per week.
Therefore, if weight loss is one of your goals, opting for a low-fat, plant-based diet may offer an advantage by naturally promoting a decrease in overall caloric intake while still providing essential nutrients for optimal human health.
NIH Study Results
The results shed light on the potential benefits and drawbacks of these two dietary approaches. Here are five key findings from the NIH study:
-
Reduced Caloric Intake: Participants who followed the low-fat plant-based diet consumed fewer calories compared to those on the low-carb animal-based diet. This suggests that adopting a plant-focused approach may naturally lead to lower energy intake, potentially making it easier for individuals striving for weight management or weight loss goals.
-
Satiety Levels: Interestingly, despite consuming fewer calories overall, participants following the low-fat plant-based diet reported feeling just as satisfied as those on the low-carb animal-based diet. This suggests that a low-fat plant-based approach can provide satiety while still promoting reduced caloric intake.
-
Nutrient Density: The study found that participants who followed the low-fat plant-based diet experienced an increase in nutrient density in their meals compared to those on the low-carb animal-based diet. This is likely due to the abundance of vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients found in whole plant foods.
-
Health Benefits: Participants following the low-fat plant-based diet showed improvements in various health markers such as cholesterol levels and blood pressure compared to those on the low-carb animal-based diet. These findings suggest that a focus on whole plant foods can have positive effects on overall health and well-being.
-
Sustainability: The study also highlighted the environmental sustainability aspect of adopting a low-fat plant-based diet over a resource-intensive animal-focused approach. By choosing more plants and less meat, individuals can contribute positively to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and preserving natural resources.
These results from the NIH study provide valuable insights into the potential advantages of a low-fat plant-based diet compared to a low-carb animal-based diet.
While individual preferences and dietary needs may vary, incorporating more whole plant foods and reducing reliance on animal products can offer numerous health benefits while also promoting environmental sustainability.
Benefits of low-fat Plant-Based Diet
One of the key benefits is weight management. Studies have consistently shown that individuals who follow a low-fat, plant-based diet tend to have lower body weight and body fat percentages compared to those on a low-carb, animal-based diet.
This can be attributed to the higher fiber content in plant-based foods and their ability to keep you feeling full for longer periods of time.
Another benefit of a low-fat, plant-based diet is the increased consumption of vegetables. Vegetables are packed with essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health and well-being.
By incorporating more vegetables into your meals, you are providing your body with an abundance of phytochemicals that can reduce cardiovascular risk factors and the risk of certain types of cancer.
Furthermore, adherence to a low-fat, plant-based diet is often easier compared to an animal-based or low-carb approach. Plant-based diets offer a wide variety of delicious options, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, which can be enjoyed in various creative ways.
On the other hand, animal-based diets may feel restrictive due to limited food choices and potential concerns about cholesterol intake.
Embracing a low-fat, plant-powered lifestyle has numerous benefits, including weight management through decreased body weight and fat percentages. Additionally, increased vegetable consumption provides essential nutrients for optimal health while reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Lastly, adherence to this type of diet is generally easier due to its versatility and abundance of flavorful options.
Disadvantages of low-carb Animal-Based Diet
A low-carb animal-based diet may have some major drawbacks that are crucial to consider. While this type of diet may initially lead to weight loss and reduced appetite, there are several disadvantages that need to be taken into account.
Firstly, a low-carb animal-based diet is typically high in saturated fats and cholesterol. Consuming excessive amounts of these can increase the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular disease risks.
Studies have shown that diets rich in animal products can raise levels of LDL cholesterol, also known as "bad" cholesterol, which can contribute to the development of plaque in the arteries. This can ultimately lead to conditions such as coronary artery disease and stroke.
Secondly, a low-carb animal-based diet often lacks essential nutrients found in plant-based foods. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts provide vital vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber that are necessary for optimal health.
By excluding or limiting these food groups from your diet, you may be missing out on key nutrients like vitamin C, vitamin E, folate, potassium, magnesium, and dietary fiber. These nutrients play important roles in supporting immune function, reducing inflammation, and promoting healthy digestion and bowel movements.
Last but equally significant is the environmental impact associated with an animal-based diet. Animal agriculture is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions and deforestation.
Meat production requires large amounts of land for livestock grazing or growing feed crops like corn or soybeans. Additionally, the water usage in raising animals for food is significantly higher than in plant-based alternatives.
In conclusion, a low-carb animal-based diet has its share of disadvantages in terms of nutrient intake. These adverse effects may include potential negative effects on cardiovascular health due to the high saturated fat content and inadequate intake of essential nutrients that are predominantly found in plant foods.
Additionally, such a diet's contribution to environmental degradation should also be considered.
Effect on Weight Loss
Switching to a healthy plant-powered eating plan can be the key to shedding those extra pounds and achieving your weight loss goals. Studies have shown that a low-fat, plant-based diet can lead to significant weight loss compared to a low-carbohydrate, animal-based diet.
In one study comparing these two diets, participants on the low-fat, plant-based diet experienced greater reductions in body weight and body fat compared to those on the low-carbohydrate, animal-based diet. The reason behind this difference in weight loss may be due to several factors.
Firstly, a low-fat, plant-based diet tends to be lower in calorie density compared to an animal-based diet. This means that you can consume more volume of food for fewer calories, leading to increased fullness and reduced overall energy intake.
Additionally, plant-based foods are often high in fiber which helps regulate blood glucose levels and promotes feelings of satiety. These beneficial effects are good news for people with Type 2 Diabetes.
Furthermore, research has shown that individuals following a low-fat, plant-based diet tend to have higher metabolic rates compared to those on a low-carbohydrate, animal-based diet.
This means that their bodies burn more calories at rest. In addition to promoting weight loss through increased energy expenditure, a high-protein intake from plant sources can also help preserve lean muscle mass during weight loss.
On the other hand, it's also essential to be mindful of processed foods. A randomized, controlled study by NIH finds ultra-processed foods cause over-eating and weight gain, in comparison to a minimally processed low fat diet such as a low-fat plant-based diet.
If you're looking for an effective way to lose weight and improve your health, consider switching to a low-fat, plant-based eating plan.
Considerations for Health
When it comes to considering the health benefits, there are important factors to take into account when comparing a low-fat, plant-based diet to a low-carb, animal-based diet.
-
Insulin Levels: One key consideration is the effect on insulin levels. A low-carbohydrate diet has been shown to lower insulin levels due to its restricted intake of carbohydrates. On the other hand, a plant-based diet that is low in unhealthy fat intake can also help regulate insulin levels by reducing excess calorie intake and improving overall metabolic function.
-
Hormone Levels: Another factor to consider is the impact on hormone levels. Research has shown that a low-carbohydrate diet can lead to changes in hormone levels, such as increased production of ketones and decreased production of insulin. In contrast, a plant-based diet can support optimal hormone balance by providing essential nutrients and phytochemicals that promote hormonal health.
-
Continuous Weeks: The duration of these diets should also be taken into account for long-term health considerations. While short-term studies have shown varying results in terms of weight loss between the two types of diets, it's important to consider how sustainable each approach may be over continuous weeks or months. A well-balanced whole food plant-based diet with adequate sources of protein and healthy fats can provide long-term health benefits by supporting weight management and overall wellness.
-
Effect on Calorie Intake: Finally, both types of diets can have an impact on calorie intake. A low-carb animal-based diet may initially result in reduced calorie intake due to its restriction on carbohydrates, leading to weight loss for some individuals. However, research suggests that over time, people tend to consume more calories when following this type of diet compared to those following a plant-based approach with an emphasis on whole food intake and nutrient density.
Additionally, a cohort study conducted on 4356 healthy participants aged over19 years old, who were followed-up for a mean duration of 3 years, has found that animal based low carbohydrate diet is associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
Whereas, multiple studies suggest that a low-fat plant-based diet such as a whole food plant-based diet has been found to be effective in the prevention and treatment of Type 2 diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a low-fat, plant-based diet provide all the necessary nutrients and proteins?
Yes, a low-fat, plant-based diet can provide all the necessary nutrients and proteins. It is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes which can meet your nutritional needs while promoting overall health and well-being.
How does a low-carb, animal-based diet affect cholesterol levels?
A low-carb, animal-based diet can have a negative effect on cholesterol levels. Research suggests that this type of diet may raise LDL (bad) cholesterol and decrease HDL (good) cholesterol, increasing the risk of heart disease.
Are there any specific health conditions that may benefit more from a low-fat, plant-based diet or a low-carb, animal-based diet?
Whether you are a healthy adult or someone with specific health conditions, a low-fat, plant-based diet such as a whole food plant-based diet has significantly more beneficial effects than any of the animal-based diets.
What are the environmental implications of following a low-fat, plant-based diet versus a low-carb, animal-based diet?
Following a low-fat, plant-based diet has positive environmental implications compared to a low-carb, animal-based diet. Plant-based diets require less land, water, and energy resources and produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions, making them more sustainable for the planet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the NIH study comparing a plant-based, low-fat diet, to a animal-based, low-carb diet, which tend to be rich on high-fat foods has provided valuable insights into the effects of these dietary approaches on ad libitum energy intake and weight management.
The results show that participants following the low-fat, plant-based diet consumed significantly fewer calories compared to those on the low-carb, animal-based diet. This statistic paints a vivid picture of how choosing a plant-based diet can lead to reduced food consumption without feeling restricted.
Furthermore, the study revealed several benefits of adopting a low-fat, plant-based diet. Not only did this dietary approach result in lower energy intake, but it also promoted weight loss and improved overall health outcomes.
By focusing on whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains while minimizing processed foods and animal products high in saturated fats and cholesterol, individuals can experience significant improvements in their well-being.
It is important to consider that there are potential disadvantages associated with a low-carb, animal-based diet as well. This type of eating pattern often leads to higher intakes of unhealthy fats and cholesterol from sources like meat and dairy products.
These components have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions. Therefore, adopting a more plant-based approach can provide individuals with not only weight management benefits but also long-term health advantages.
To incorporate more plant-based options into your daily meals, start by gradually replacing meat with plant protein sources such as beans or tofu. Additionally, aim for at least five servings of fruits and vegetables each day while including whole grains like quinoa or brown rice for added fiber and nutrients.
Remember that making small changes over time can lead to sustainable habits that promote optimal health outcomes.
Overall, this study highlights the effectiveness of a low-fat, plant-based diet in reducing energy intake while promoting weight loss and improving overall health outcomes.
By choosing whole foods over processed alternatives and minimizing animal product consumption high in unhealthy fats and cholesterol, individuals can make significant strides towards achieving their health goals.
Embracing a plant-based lifestyle not only benefits personal well-being but also contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly world.
Next Steps
Congratulations! Now you know the impact a low-fat plant-based diet and a low-carbohydrate animal-based diet has on your health, where a low-fat plant-based diet emerge as the clear winner!
Here are some fantastic tools to guide you through a smooth transition to a healthier lifestyle and overall well-being:
- Book an online consultation with Dr. Achyuthan Eswar for a personalized medical consultation to prevent, treat and better manage lifestyle diseases through diet and lifestyle.
- Learn to cook delicious whole food plant based goodies and sign up for courses on health and wellness from the comfort of you home. Join our online courses from anywhere in the world.
- Get daily essentials to cook healthy meals at home.
- Stock up on delicious sweets and snacks that are sugar/jaggery-free, oil-free, maida-free and plant-based - Available Pan-India.