My grandmother passed away from Dementia and Parkinson's Disease.
These are diseases that we must do everything we can to prevent.
It may be too late for her, but I hope this article helps you and your loved ones live longer, healthier lives.
Top Brain Healthy Food
Brain food is something everyone wants to eat. But does it really matter what foods you eat to improve your brain health?
Your brain is responsible for
- Processing information
- Learning new things
- Remembering important details
- Controlling emotions
- And practically keeping your body alive!
If you want to stay sharp, focus, and perform at your peak level, then you should take steps to ensure your brain is functioning optimally at the cellular and molecular level.
It’s true that certain foods have beneficial effects on your brain power and brain health.
Some studies suggest that consuming blueberries, green tea, and other natural antioxidants have beneficial effects on cognition.
Other research suggests that omega-3 fatty acids found in flaxseeds is one of the dietary factors that can also improve brain function.
Recent studies show that an unhealthy diet can actively cause neurocognitive decline too.
Apart from Alzheimer's Disease and dementia, other brain diseases like epilepsy, Vitamin B12 deficiency, and Parkinson's disease are on the rise too.
The good news is, lifestyle changes can significantly help prevent and potentially treat most of these conditions.
Cognitive Decline & Alzheimer's Disease
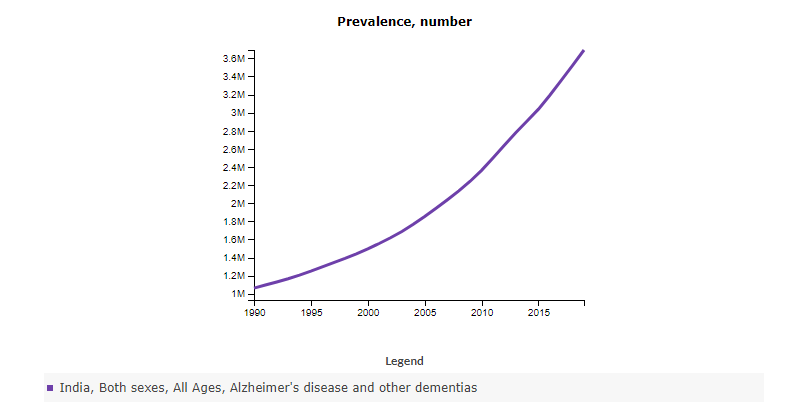
Speaking of neurocognitive decline, Alzheimer's Disease rates are steadily climbing up in India.
We have traditionally enjoyed great protection from dementia, but we are losing that protection today.
Today, we have more than 3.5 times the number of people with Alzheimer's Disease than we did in 1990.
Source: healthdata.org
Lifestyle changes can go a long way in preventing Alzheimer's Disease. Here's what we know so far:
- A Mediterranean diet may reduce risk of Alzheimer’s. It may also reduce risk of death from Alzheimer's disease.
- Different fruits and vegetables have positive effects on different brain functions. This is why it's important to eat more variety of fruits and vegetables. But how much to eat?
- The more fruits and vegetables you eat, the lower your risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
- Even fruit and vegetable juices may work, reducing your risk of developing Alzheimer’s by 76%.
- If you eat blueberries and strawberries, great! They are associated with postponing cognitive aging by a whopping 2.5 years! This may be due to their Ellagic acid content.
- Strawberry milkshakes or yogurt don't count though! Ellagic acid does not get absorbed if you consume berries along with milk or other dairy products.
- There is a link between tofu and dementia, but not because of the tofu itself.
- It is because tofu can be contaminated with formaldehyde sometimes, and this increases dementia risk.
- Ensure to get your tofu fresh from a trusted source!
- Does coconut oil work?
- There is not much evidence that shows this.
- In fact, coconut oil consumption may contribute to atherosclerosis, one of the driving factors behind Alzheimer's Disease
- Saffron spice seems to have some beneficial effects. A study showed that it works as well as Aricept, a leading Alzheimer's drug, but without the drug's side effects.
- Using turmeric and restricting meat has been a hallmark of traditional Indian cuisine compared to the West.
- This may have amplified our protection from both Alzheimer's as well as Parkinson's Disease.
- However, curcumin supplements do not appear to help.
- Some more food-related risks linked with neurocognitive decline and parkinson's disease include:
- Metals like aluminum and iron accumulation
- Glycotoxins in chicken
- BMAA, a neurotoxin in seafood
- Other toxins and even natural hormones found in milk, even skim milk
So what are some of the top brain healthy foods that you can get your hands on today?
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Rich Nuts & Seeds
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that play a vital role in maintaining good health.
They support heart health, improve vision, enhance mental health, immune system health, promote healthy brain function,boost brain development, and help prevent heart disease, arthritis, diabetes, cancer, depression, dementia, and skin conditions. They may slow age-related mental decline.
Omega-3 fatty acids are found in nuts and seeds.
Interestingly, the omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) stimulates neuronal plasticity through the Akt pathway , suggesting that Akt activation might be crucial for integrating the effects of food-derived signals on brain plasticity. (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
Omega-3 fatty acids also benefit children's cognitive development. In addition, they can help prevent ADHD symptoms in kids.
Omega-3s are considered essential fatty acids, meaning our bodies cannot produce them and they need to come from food sources. They are found mainly in:
-
walnuts
-
flaxseeds
-
chia seeds
-
hemp seeds
-
pumpkin seeds
A lot of people opt for omega-3 supplements. However, this has been shown not to have the purported benefits.
You can get all the omega-3 fatty acids your brain needs for optimal health from plant foods. This includes both short-chain and long-chain omega-3 fatty acids.
Leafy Greens
Leafy green vegetables are packed full of vitamins and minerals that have proven benefits for brain health. These include Vitamin K, Lutein, Folate, and Beta Carotene.
Research shows that eating leafy greens helps slow down the rate at which our brains age. Studies show that older adults who eat more leafy greens have better memory and thinking skills than those who don't.
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition published a study where researchers followed over 1,000 elderly men for 12 years. They found that participants who ate more leafy greens had less cognitive decline than those who didn't.
In addition to helping prevent neurocognitive decline, numerous studies suggest that eating leafy greens may improve mental function. In fact, one study showed that women who consumed the highest amounts of leafy greens had higher scores on tests measuring verbal fluency than those who ate the least amount.
So next time you're craving a salad, consider adding some leafy greens to your plate. Not only will you enjoy the taste, but you'll be getting some extra brain power along with it!
Fruits
Vitamin C is essential for survival. Thankfully, whole plant foods are bursting with vitamin C!
Some fruits like oranges, kiwi, tomatoes, strawberries, guava and amla contain high levels of vitamin C.
Citrus fruits help enhance blood supply to all parts of the body.
However, orange juice may cause a spike in blood sugar and oxidative damage. Whole oranges may be a healthier option.
Bananas contains potassium, an important mineral that helps regulate nerve impulses and muscle contractions. Potassium also helps maintain fluid balance within cells, which may help prevent memory loss.
Fruits like apples, pears, oranges, grapes, cherries, peaches, plums, and apricots are packed with antioxidants, which help protect your brain from free radicals, molecules that damage cells. Antioxidants also help keep your blood vessels healthy and prevent brain stroke.
Fruit contains other nutrients too. These include fiber, potassium, and antioxidants. Fiber helps reduce cholesterol and blood pressure. Potassium helps maintain fluid balance and electrolyte levels. Antioxidants help protect the body against free radicals. Free radicals are molecules that damage DNA and cause brain cell damage.
So by eating fruit regularly, we can improve our overall health and reduce the risk of diseases like Alzheimer's.
Leafy Vegetables
Brain cells communicate with each other through electrical impulses. These impulses travel along nerves and are transmitted from one nerve cell to another via chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. When you eat foods containing certain nutrients such as vitamin B6, magnesium, folate, or zinc, they help produce these chemicals.
Leafy greens contain high levels of folate (vitamin B9), an important nutrient for healthy cells. Folate helps produce DNA and RNA, two building blocks of cells. It also plays a role in cell division and repair.
Leafy vegetables contain high levels of vitamin K, folate, and potassium. They also contain antioxidants that may protect against Alzheimer's disease.
Leafy vegetables contain high levels of antioxidants, such as lutein and zeaxanthin, which help protect against age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
1. Spinach
Spinach has been shown to have high levels of magnesium, lutein, zeaxanthin, and beta-carotene, which are all antioxidants that protect your brain from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are molecules that can cause damage to cells and DNA. This may help explain why people who eat grreens regularly tend to live longer than those who don't.
Low magnesium levels are linked to many neurological diseases, including migraine, depression, and epilepsy.
2. Kale
Kale contains many vitamins and minerals like vitamin A, C, E, B6, folate, iron, calcium, magnesium, zinc, selenium, copper, manganese, and omega fatty acids. All these nutrients are beneficial to our health. They keep us healthy and prevent diseases.
3. Broccoli
Broccoli is rich in fiber, vitamin C, vitamin K, folate, thiamine (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin, pantothenic acid, biotin, and dietary fiber. These nutrients are essential for proper digestion, energy production, and maintaining a strong immune system. Eating broccoli helps lower cholesterol and blood pressure.
Broccoli is packed with powerful plant compounds, including antioxidants and sulphoraphane precurcors. These are potent anti-cancer molecules.
It is also very high in vitamin K, delivering more than 100% of the Recommended Daily Intake (RDI) in a 1-cup (160-gram) serving of cooked broccoli.
This fat-soluble vitamin is essential for forming sphingolipids, a type of fat that's densely packed into brain cells.
A few studies in older adults have linked a higher vitamin K intake to better memory and cognitive status.
Beyond vitamin K, broccoli contains a number of compounds that give it anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, which may help protect the brain against damage.
Broccoli contains a number of compounds that have powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, including vitamin K. (healthline.com)
Here's how you can eat more leafy greens
1. Add them to your salad!
A healthy dose of leafy greens can help boost your immune system, lower blood pressure, and improve overall health. They are packed with vitamins A, C, K, and folate, along with calcium, iron, magnesium, and fiber. Try adding spinach, kale, collard greens, arugula, chard, mustard greens, turnip greens, or any other variety to your salads.
2. Make smoothies!
Smoothies are great ways to get plenty of vegetables into your diet.
You can add leafy greens like kale, spinach, romaine lettuce, or collards to your blender.
Blend until they’re completely broken down, then pour into glasses and enjoy!
If you enjoy sweet smoothies, add some fruits, like banana, apple, papaya or grapes.
If you enjoy savoury smoothies, add some vegetables, like cucumber, carrot or beetroot.
You can even do both!
Try amla and spices too.
3. Include them in soups!
Soups are a great way to incorporate veggies into your meals.
Add some leafy greens like kale or spinach to your soup to give it flavor and nutrition.
4. Add them in lentil dishes!
Palak dal, keerai sambar, palak pappu, soppu saaru, chole palak... there are many traditional dishes bursting with greens.
Adding greens in your dal dishes is a great way to move closer to a balanced diet.
5. Make chutneys!
The best part about chutneys is that you can stuff it chock-full of greens and yet they taste amazing!
Try coriander chutney, pudina chutney or pirandai chutney.
6. Try baked snacks with green leafy vegetables
Do you love pakoda, vada and cutlet as much as I do? Then you must try these.
Try baking them instead of frying them.
The trick is to add some nuts and nut butter to the batter so it is moist and rich even when baked.
Baked snacks are a great hiding place for greens. Everyone loves them!
Berries
Antioxidant-rich berries that can boost brain health include:
- strawberries
- blackberries
- blueberries
- blackcurrants
- mulberries
- gooseberries
Strawberries are loaded with antioxidants that help fight free radicals in your body.
Antioxidants protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can harm healthy cells.
Free radicals can lead to diseases such as Alzheimer's disease.
Blackberry has been used for thousands of years to treat depression, anxiety, stress, insomnia, and other mental health issues.
The berries contain high levels of antioxidants called anthocyanins which help to reduce inflammation in the body.
This helps to relieve symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Blueberries are one of the best foods for our brains.
They contain high levels of antioxidants and fiber.
They may also help prevent Alzheimer’s disease and boost memory.
Some of the antioxidants in blueberries have been found to accumulate in the brain and help improve communication between brain cells.
Blackcurrants are great for our brains because they contain high levels of vitamins and antioxidants such as vitamin C and anthocyanins.
These antioxidants help protect against damage from free radicals.
Free radicals are molecules that cause cell damage and can lead to diseases like cancer.
Mulberry trees are native to China, India, and Pakistan, where they grow in subtropical climates.
The leaves of these trees contain high levels of antioxidants, which help protect against free radicals.
Antioxidants are essential nutrients that help prevent damage caused by oxidation, such as aging, stroke, dementia and cancer.
Amla or Indian Gooseberry contains a lot of vitamin c, which helps body produce norepinephrine. This improves memory.
Norepinephrine is a neurotransmitter that improves brain function especially in people suffering from dementia.
To say Amla contains phytonutrients and antioxidants would be an understatement.
Amla has the highest antioxidant concentration of all foods in the world tested until today!
It can help fight off free radicals that can harm brain cells and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases, heart disease and many other debilitating conditions.
Green Vegetables
Green Vegetables such as:
- Spinach
- Cauliflower
- Kale
- Turnip greens
- Collard greens
- Mustard greens
- Amaranthus leaves
- Chakotha leaves
- Paruppu Keerai leaves
- Coriander leaves
- Mint leaves
- Curry leaves
- Sorrel leaves or gongura
- Malabar spinach leaves or basale soppu
contain nutrients that help protect against Alzheimer's disease.
They also provide fiber, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytochemicals.
These nutrients may slow down the progression of the disease or even prevent it altogether.
Avacados are rich in healthy fats. Healthy fats have amazing brain power: A diet with higher levels of them has been linked to lower dementia and stroke risks and slower mental decline; plus, they may play a vital role in enhancing memory, especially as we get older. (webmd.com)
Turmeric
Turmeric may help improve memory and attention. Curcumin boosts levels the brain hormone BDNF. This helps grow new neurons and may help combat various degenerative processes.
Turmeric has been used for thousands of years in Ayurvedic medicine, especially for its anti-inflammatory properties.
Turmeric contains curcuminoids, including turmerones and bisdemethoxycurcumin, both of which are responsible for turmeric's health benefits.
Curcuminoids have powerful antioxidant activity that helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Free radicals can cause inflammation, which is why turmeric may help reduce swelling and pain associated with arthritis, apart from being great for brain health.
FAQ on Brain Healthy Food
How does Food affect Cognitive Function?
The combination of certain brain healthy diet and exercise can have additive effects on synaptic plasticity and cognitive function.
Molecules that could explain the synergistic effects of diet and exercise include BDNF, which has emerged as an important factor for translating the effects of exercise on synaptic plasticity and cognitive function , and several molecules that are associated with the action of BDNF on synaptic function, such as synapsin I, calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and cyclic AMP-responsive element (CRE)-binding protein (CREB). (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
Is Dark Chocolate Good for our Brain?
Dark chocolate and cocoa powder are packed with a few brain-boosting compounds, including flavonoids, caffeine, and antioxidants. Studies have suggested that eating chocolate, especially dark chocolate, could boost both memory and mood. (healthline.com)
Uma Naidoo , a nutritional psychiatrist, faculty member at Harvard Medical School and author of "This Is Your Brain on Food, says, "Extra dark chocolate is full of antioxidants and cacao flavanols that help preserve the health of brain cells," Naidoo tells CNBC Make It. "It also contains fiber to help reduce brain inflammation prevent cognitive decline 2020 study looked at how dark chocolate and white chocolate can affect the memory of healthy young adults. (cnbc.com)
However, the other ingredients of chocolate apart from cocoa beans may have detrimental effects on health. For best results, choose 100% dark chocolate or buy your own cocoa beans and grind them at home.
What diet helps to maintain a healthy brain?
To promote healthy brain aging and stave off neurocognitive diseases of aging including dementias. Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and memory loss, there is good reason to believe that a well-balanced, nutritious whole-food plant-based diet can provide many benefits. (pacificneuroscienceinstitute.org)
How to cure brain fog?
Iron deficiency is often characterized by brain fog and impaired brain function. (healthline.com)
The brain uses zinc for nerve signaling, magnesium for learning and memory, copper for controlling nerve signals, and iron to prevent brain fog. (premierneurologycenter.com)
Eating too few healthy carbs, even whole whole grains like brown rice, and starving oneself may lead to brain fog and irritability. (bbcgoodfood.com)
How to prevent brain shrinkage?
Leafy Greens are a good source of B vitamins: vitamin B-6 and vitamin B-12.
Recent research suggests that these vitamins may prevent brain shrinkage and delay cognitive decline. (medicalnewstoday.com)
Does Alcohol provide any brain benefit?
Recent mendelian randomisation studies have shown that no amount of alcohol is healthy for you. Even small quantities of alcohol like a glass of wine every week could increase your risk of disease and mortality.
In Parkinson's disease, patients may have balance issues, which could worsen with alcohol. (pacificneuroscienceinstitute.org)
Try drinking herbal teas. A recent study said that regular tea drinkers may have an advantage over non-drinkers, wherein they may have a better brain structure. (food.ndtv.com)
Is Western Diet consisting of Meat Products Bad for our Brain?
A typical Western diet often increases cardiovascular disease risk, possibly contributing to faster brain aging. (nia.nih.gov)
How to prevent age-related neurodegenerative disease?
The antioxidants in berries include anthocyanin, caffeic acid, catechin, and quercetin.
A 2014 review notes that the antioxidant compounds in berries have many positive effects on the brain, including:
- Improving communication between brain cells
- Reducing inflammation throughout the body
- Increasing plasticity, which helps brain cells form new connections
- Boosting learning and memory
- Reducing or delaying age-related neurodegenerative diseases
- Cognitive decline.
Antioxidant-rich berries that can boost brain health include: strawberries, blackberries, blueberries, blackcurrants, mulberries, and gooseberries.
Some may also reduce the risk of stroke and age-related neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, for which your diet is an important risk factor. (medicalnewstoday.com)
Why do people suffer from age-related cognitive decline?
Antioxidants are especially important for brain health, as the brain is highly susceptible to oxidative stress, which contributes to age-related cognitive decline and brain diseases. (medicalnewstoday.com)
How does nutrients in foods affect our brain?
Well-established regulators of synaptic plasticity, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor BDNF, can function as metabolic modulators, responding to peripheral signals such as food intake.
ATP produced by mitochondria might activate brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1), which support synaptic plasticity and cognitive function. (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
Curcumin boosts brain-derived neurotrophic factor, a type of growth hormone that helps brain cells grow. (healthline.com)
It has long been suspected that the relative abundance of specific nutrients can affect cognitive processes and emotions. For instance, a diet that is rich in omega-3 fatty acids is garnering appreciation for supporting cognitive processes in humans and upregulating genes that are important for maintaining synaptic function and plasticity in rodents. (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
Are Oranges Help Improve Brain Health?
A study published in the American Journal of clinical nutrition has pointed out that the adults who have taken part in a research that asked them to consume oranges daily showed an overall improvement in global cognitive functioning. (food.ndtv.com)
What is a typical brain-boosting food?
Brain-boosting foods tend to contain one or more of the following:
- Antioxidants, such as flavonoids or vitamin E B vitamins
- Healthful fats such as a balance between omega 3 & omega 6 fatty acids
Beyond adjusting the diet, a person can optimize their brain function by:
- not eating too much or too little
- Getting enough sleep
- Keeping hydrated
- Exercising regularly
- Reducing alcohol intake
Eating a brain-boosting diet will also provide many benefits for the entire body. (medicalnewstoday.com)
Are exercises important?
In some studies, physical activity has been linked to improved cognitive performance and reduced risk for Alzheimer's disease. (nia.nih.gov)
Are Beans any good?
Kidney and pinto beans are good choices as they contain more omega-3 fatty acids than other bean varieties, which are important for brain growth and function. (onhealth.com)
How to increase memory performance with foods?
IGF1 can signal to neurons in the hypothalamus and the hippocampus, with resulting effects on learning and memory performance. Polyphenols have been shown to increase hippocampal plasticity. (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
Polyphenols are micronutrients that naturally occur in plants.
They are also easy to get in your diet from foods like fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices.
There are more than 8,000 types of polyphenols, which include flavonoids like quercetin and catechins in fruits. (webmd.com)
Is there a connection between diabetes and manic depression?
In a large study of patients with manic depression , the rate of diabetes was found to be higher than in the general population (1.2% of people aged 18–44 years and 6.3% of people aged 45–64 years).
The overall prevalence of diabetes in a group of 95 patients with schizophrenia was 15.8%, and this increased to 18.9% with age , whereas diabetes in 203 patients with manic depression ranged from 2.9% in patients of approximately 30 years of age to 25% in patients of 75–79 years of age.
However, it is difficult to ascertain a cause–effect relationship between diabetes and psychiatric disorders in these studies given that schizophrenia, major depression and other psychiatric disorders are associated with poor quality of life and the side effects of anti-psychotic medication. (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
Can Lifestyle Changes Improve Cognitive Capacity?
A recent study in a rodent model of depression demonstrated that depressive manifestations and subsequent antidepressant treatment are associated with sustained changes in histone acetylation and methylation at BDNF promoter III.
These studies represent a starting point for understanding how intracellular signalling that is triggered by lifestyle factors can promote lasting changes in DNA function in the brain and in cognitive capacity. (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
How to Get Started with Brain Healthy Food?
If you are looking to prevent or postpone neurocognitive decline, getting started with brain healthy food today is a great idea.
- Try a Plant-based Meal from Sampoorna Ahara home delivered and discover how tasty healthy food can be.
- Join the Plant Based Diet Masterclass on NutritionScience.in and master the art of plant based nutrition and cooking from the comfort of your home.
I hope this article is helpful for you and your family. Please do share it with your loved ones so that they may benefit as from eating healthier as well.
Be Blessed!
Dr Achyuthan Eswar
Co-founder, NutritionScience.in & SampoornaAhara.com
This article contains general information about brain healthy foods. It is not a substitute for personal medical advise from a health care professional like your doctor. Please consult your doctor for any diagnosis or medical advise you may require.
Sources
- https://nutritionfacts.org/topics/brain-health/
- Barnes DE, Yaffe K. The projected effect of risk factor reduction on Alzheimer's disease prevalence.Lancet Neurol. 2011;10(9):819-828. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70072-2
- Scarmeas N, Luchsinger JA, Mayeux R, Stern Y. Mediterranean diet and Alzheimer disease mortality. Neurology. 2007;69(11):1084-1093. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000277320.50685.7c
- Hughes TF, Andel R, Small BJ, et al. Midlife fruit and vegetable consumption and risk of dementia in later life in Swedish twins. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2010;18(5):413-420. doi:10.1097/JGP.0b013e3181c65250